The Ultimate Guide to Greywater Recycling Systems and Their Benefits
Greywater recycling systems explained can transform how you use water at home. These systems collect and treat wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry, allowing you to reuse it for irrigation or toilet flushing. This greywater use not only conserves water but also reduces your utility bills and environmental impact, as the greywater system diverts waste, benefiting a business greywater recycling system and utilizing greywater treatment systems.
Understanding these systems is crucial for anyone interested in sustainable living. They are easy to install and maintain, making them a practical choice for homeowners. With the right system, you can make a significant difference in your water usage without compromising comfort. Dive into the benefits and options available to see how greywater recycling can enhance your lifestyle day by day while protecting our planet.
Key Takeaways
-
Greywater recycling systems collect and reuse water from sinks, showers, and washing machines, helping to conserve freshwater resources.
-
Understanding how these systems work is crucial; they typically involve filtration and treatment processes to ensure the water is safe for non-potable uses like irrigation.
-
The benefits of greywater recycling include reduced water bills, lower environmental impact, and sustainable water management practices.
-
Consider the initial costs and potential savings when evaluating greywater systems; while installation can be expensive, long-term savings on water bills may offset this.
-
Be aware of local regulations and installation requirements for greywater systems to ensure compliance and proper functioning.
-
Address common concerns about safety and maintenance by researching different types of greywater systems that best fit your needs and lifestyle.
What is Greywater Recycling
Definition
Greywater refers to non-fecal wastewater generated from domestic activities. This includes water from sinks, showers, bathtubs, and washing machines. It does not include water from toilets, which is classified as blackwater day. Greywater typically contains soap, dirt, and food particles.
Purpose
The main purpose of greywater recycling day is to promote sustainable water use. By treating and reusing this type of water, households can significantly reduce their overall water consumption. This is especially important in areas facing water scarcity. Recycling greywater can help conserve fresh water supplies for drinking and cooking.
Treatment Needs
Greywater requires less intensive treatment than blackwater. Blackwater contains harmful pathogens and requires advanced treatment methods to ensure safety. Greywater can often be treated with simpler processes like filtration and disinfection day.
Benefits
-
Water Conservation: Recycling greywater reduces the need for fresh water.
-
Cost Savings: Lower water bills result from decreased consumption.
-
Environmental Impact: Less demand on local water sources helps protect ecosystems.
Examples of Use
Many homes use greywater systems for irrigation purposes. For example, a household might direct shower water to their garden during the day. This practice supports plant growth while minimizing waste.
Systems in Place
Various greywater recycling systems exist today. Some are simple and involve basic filtration methods. Others are more complex, utilizing multiple steps to ensure safety and efficiency. Homeowners can choose a system based on their needs, gray water options, and local regulations day by day.
Regulations
Local regulations often dictate how greywater can be reused. Some areas allow it for irrigation but prohibit its use indoors without proper treatment. Homeowners should check their local laws day before installing a greywater system.
Maintenance
Proper maintenance is crucial for any greywater system. Regular checks prevent clogs and ensure effective operation. Homeowners should clean filters and inspect pipes periodically.
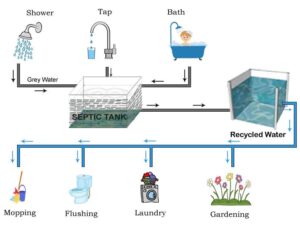
How Greywater Systems Work
Collection Process
Greywater systems collect water from various household sources. Common sources include sinks, showers, and washing machines. This water is often called untreated greywater because it has not gone through any purification process yet, day.
A home greywater system usually connects directly to these fixtures day. Pipes redirect the used water into a separate tank. This method prevents the greywater from mixing with sewage. This separation is crucial for effective recycling.
Treatment Steps
Once collected, the greywater undergoes treatment day to make it safe for reuse. The first step involves basic filtration. Filters remove large particles like hair and food debris.
Next, a more advanced water treatment system may use biological processes. Beneficial bacteria break down organic matter in the greywater. This step significantly reduces harmful pathogens.
e systems utilize chemical treatments as well. Chlorination or UV light can kill remaining bacteria and viruses. These methods ensure that the treated water meets safety standards.
Storage Options
After treatment, storing the purified greywater is essential before reuse. Many systems include storage tanks specifically designed for this purpose. These tanks are sealed to prevent contamination.
The size of the storage tank depends on the amount of greywater generated. A typical home greywater system might need a tank that holds 200-500 gallons. Larger businesses may require much bigger tanks.
Treated greywater can be reused for various applications. A landscape greywater system often uses it for irrigation purposes. Using recycled water in gardens helps conserve fresh water resources.
In summary, greywater recycling systems provide an efficient way to manage water in homes and businesses. By collecting, treating, and storing this valuable resource, these systems promote sustainability and reduce environmental impact.
Benefits of Greywater Recycling
Water Savings
Greywater recycling systems offer significant reductions in overall water consumption. By reusing water from sinks, showers, and washing machines, households can decrease their reliance on freshwater sources. Studies show that homes can save up to 50% of their water usage through greywater recycling. This reduction is crucial in areas facing water scarcity.
Businesses also see the benefits. Implementing greywater systems can lead to lower operational costs. For example, restaurants and hotels can reduce their water bills significantly. Lower costs allow these businesses to invest more in other areas, enhancing overall efficiency.
Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of greywater recycling are substantial. These systems help reduce the carbon footprint associated with water treatment processes. Traditional wastewater treatment requires energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. By recycling greywater, we minimize the energy needed for treating fresh water.
Moreover, greywater recycling projects contribute to sustainable water management practices. They help preserve natural water bodies by reducing the amount of wastewater discharged into them. Consequently, local ecosystems benefit from cleaner waterways.
Purpose of Greywater
The primary purposes of greywater include irrigation and toilet flushing. Using recycled water for these activities conserves potable water for drinking and cooking. This practice promotes a more sustainable lifestyle.
Many municipalities encourage the use of recycled water in landscaping. Parks and gardens can thrive on treated greywater, leading to lush green spaces without straining freshwater supplies. This shift not only supports urban greenery but also fosters community well-being.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Investing in greywater recycling systems proves to be a cost-effective solution over time. Initial setup expenses may seem high, but long-term savings outweigh them. Homeowners and businesses who adopt these systems often recoup their investments within a few years.
Government incentives further enhance affordability. Many regions offer rebates or tax credits for installing greywater systems. These financial aids make it easier for individuals and organizations to transition toward sustainable practices.
Cost of Greywater Systems
Installation Factors
Several factors influence the installation costs of greywater systems. The type of system selected plays a vital role. Simple systems, like diverters, are generally cheaper. In contrast, more complex systems with advanced filtration and treatment processes can be significantly more expensive.
The size of the system also affects the cost. Larger homes require bigger systems to handle increased water flow. This often means higher installation costs. Local building codes may dictate specific requirements, which can add to expenses.
Long-term Savings
Investing in a greywater recycling system can lead to substantial long-term savings on water bills. Households that recycle greywater can reduce their overall water usage by up to 50%. This reduction translates into lower monthly utility bills.
For example, if a family spends $100 per month on water, they could save $600 annually by using greywater systems. Over time, these savings can offset the initial installation costs. Many homeowners find that their investment pays off within a few years due to reduced water expenses.
Financial Incentives
Various financial incentives exist for those adopting greywater systems. Some states offer tax relief or rebates for installing these eco-friendly systems. These incentives can significantly lower upfront costs.
Homeowners should research local programs that support greywater recycling initiatives. Some municipalities provide grants or low-interest loans specifically for these installations. These financial aids encourage more people to consider greywater systems.
Maintenance Costs
While installation costs are significant, ongoing maintenance is another factor to consider. Regular upkeep ensures that the system operates efficiently and safely. Maintenance costs vary depending on the system’s complexity and size.
Basic systems may require minimal maintenance, while advanced setups might need professional servicing periodically. Homeowners should budget for these potential expenses when planning their greywater system investments.
Environmental Impact
Choosing to install a greywater recycling system not only saves money but also benefits the environment. By reusing water for irrigation or toilet flushing, households reduce their demand on municipal water supplies. This practice helps conserve precious resources and decreases wastewater production.
Communities benefit from reduced strain on local sewage systems as well. When more homes recycle greywater, less treated water enters treatment facilities. This leads to improved environmental health and sustainability.
Installation Requirements
Planning Importance
Planning is crucial for greywater recycling systems. It should occur during the building design phase. This early planning helps integrate the system seamlessly into the structure. Proper planning can reduce installation costs and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Designers must consider the layout of appliances that will use greywater. They need to identify where greywater will be collected and reused. This foresight maximizes the efficiency of the system. It also ensures that plumbing and drainage are correctly configured.
Role of Technical Account Managers
Technical account managers play a vital role in overseeing installations. They ensure that all components meet industry standards. Their expertise helps prevent costly mistakes during the installation process.
These professionals coordinate between builders, suppliers, and installers. They provide guidance on best practices for system setup. Their involvement can lead to smoother operations and fewer issues down the line.
Account managers also help in selecting appropriate platforms for greywater systems. They assess site conditions and recommend solutions tailored to specific needs.
Maintenance Necessity
Regular inspections are essential for maintaining greywater recycling systems. These inspections ensure compliance with health and safety regulations. They also help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Maintenance involves checking all components of the system, including pumps, filters, and tanks. Technicians must verify that everything operates efficiently. Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of the system and reduces long-term costs.
Without proper maintenance, systems may fail or become less effective over time. Routine checks can catch problems early, saving money on repairs later.
Greywater vs Other Reuse Systems
Internal Sources
Greywater systems focus on internal water sources. They collect water from sinks, showers, and washing machines. This water is usually less contaminated than other types.
In contrast, rainwater harvesting captures rain from roofs and surfaces. It stores this water for various uses. Rainwater systems rely on external sources rather than internal ones.
Both systems help conserve water. However, greywater recycling systems are designed specifically for indoor use.
Treatment Complexity
The treatment of greywater differs significantly from blackwater. Greywater contains fewer pathogens and contaminants. This makes it easier to treat compared to blackwater, which comes from toilets.
Blackwater requires advanced treatment methods. These methods often include anaerobic digestion or complex filtration systems. Greywater treatment systems can use simpler filters and processes.
For example, greywater filters can remove hair and soap residues efficiently. These filters do not need as much maintenance as those used for blackwater systems.
Return on Investment
Greywater systems offer a quicker return on investment. They reduce water bills by reusing water that would otherwise go down the drain. Homeowners can save money on both water and sewage costs.
The installation of a greywater system may seem costly upfront. However, savings accumulate over time. Many households notice reduced utility bills within months of installation.
The initial investment pays off as homeowners see lower monthly expenses. In some cases, rebates and incentives are available to offset installation costs.
Additional Benefits
Reusing greywater helps in reducing overall water consumption. This practice conserves precious resources, especially in drought-prone areas.
Greywater can be reused for irrigation or toilet flushing. This dual-purpose use maximizes its value and reduces waste.
Rainwater recycling systems also have their benefits but differ in application. While they provide an alternative source of water, they depend on weather conditions.
In regions with limited rainfall, relying solely on rainwater can be risky. Greywater systems provide a more consistent source of reusable wastewater.
Common Concerns and Questions
Safety Misconceptions
Many people worry about the safety of using recycled greywater. They often think it is dirty or contaminated. However, when treated properly, greywater can be quite clean. Treatment processes remove harmful contaminants. This makes it safe for non-potable uses like irrigation or toilet flushing.
Misunderstandings about cleanliness lead to fear. Some believe that using recycled water will cause health issues. In reality, studies show that with proper treatment, these risks are minimal. Greywater recycling systems can operate safely in homes and businesses alike.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory considerations play a significant role in greywater recycling systems. Different regions have specific laws governing their use. Homeowners must check local regulations before installation. Many areas require permits for greywater systems.
Compliance ensures safety and effectiveness. It also protects public health by ensuring proper treatment methods are used. Businesses looking to invest in greywater systems must also consider these regulations. Failure to comply can result in fines or system removal.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is essential for greywater systems. Owners should perform routine checks on collection units and tanks. This helps identify any issues early on. Keeping filters clean is crucial for effective treatment.
Adjusting pressure levels is another important task. If pressure drops too low, it can affect water flow. Regular monitoring allows for timely actions to maintain optimal performance.
Businesses that rely on greywater must account for consumption patterns as well. Understanding how much water is used can help optimize the system’s efficiency. This knowledge aids in making informed decisions about water usage and potential savings.
Investment and Savings
Investing in greywater recycling systems can lead to significant savings over time. While initial costs may seem high, the long-term benefits outweigh them. Reduced water bills result from decreased reliance on municipal water supply.
Properties equipped with efficient greywater systems may see increased value. Potential buyers often view these features favorably, knowing they reduce overall water consumption.
Batch treatment methods can also enhance efficiency. These systems treat collected greywater in batches rather than continuously. This approach can save energy and resources while maintaining effectiveness.
Types of Greywater Systems
Treatment Methods
Greywater systems can be categorized by their treatment methods. Passive systems use natural processes to filter and clean water. These systems often rely on gravity and soil filtration. They are simpler and require less energy.
Active systems involve mechanical processes. They typically use pumps and filtration units to treat the greywater. These systems are more complex but can provide higher quality water for reuse. They often include additional components like UV lights or chemical treatments.
Residential vs. Commercial
Residential greywater systems focus on single-family homes. They usually handle smaller volumes of water from sinks, showers, and laundry. Homeowners often install simple passive systems for easy maintenance.
Commercial greywater systems deal with larger volumes of wastewater. They serve businesses, restaurants, and hotels. These systems require more advanced technology due to the higher flow rates and stricter regulations. Businesses may need active systems to meet health standards.
Emerging Technologies
New technologies are improving greywater recycling efficiency. One example is smart sensors that monitor water quality in real-time. These sensors help optimize treatment processes.
Another innovation is membrane bioreactors (MBRs). MBRs combine biological treatment with membrane filtration. This process produces high-quality recycled water suitable for various uses.
Nanotechnology is also making strides in greywater treatment. It enhances the removal of contaminants at a microscopic level. This technology can lead to cleaner water with fewer chemicals.
Benefits of Greywater Systems
Greywater recycling offers several benefits:
-
Reduces water consumption
-
Lowers utility bills
-
Decreases environmental impact
-
Provides irrigation for landscaping
These advantages make greywater systems appealing for both residential and commercial applications.
Regulations and Standards
Local regulations govern greywater reuse practices. Compliance ensures safe usage and prevents contamination risks. Many regions have specific guidelines about what types of greywater can be reused and how it should be treated.
Homeowners and businesses must understand these rules before installing a system. Consulting local authorities can help clarify requirements.
Closing Thoughts
Greywater recycling systems offer a smart solution for conserving water and reducing waste. By understanding how these systems work, you can tap into their benefits, from cost savings to environmental impact. Whether you’re considering installation or just curious about the options, knowing the ins and outs helps you make informed choices.
Don’t let misconceptions hold you back. Embrace greywater recycling to enhance your sustainability efforts. Start exploring ways to implement these systems in your home or community today. The future of water conservation is in your hands—take action now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is greywater?
Greywater is wastewater generated from household activities like washing dishes, laundry, and bathing. It excludes water from toilets, which is classified as blackwater. Greywater can be recycled for irrigation and other non-potable uses.
How does a greywater recycling system work?
A greywater recycling system collects, filters, and treats used water from sinks, showers, and washing machines. The treated greywater is then reused for irrigation or toilet flushing, conserving fresh water resources.
What are the benefits of greywater recycling?
Greywater recycling reduces water consumption, lowers utility bills, and minimizes environmental impact. It also helps maintain landscape health by providing a consistent water source.
Are greywater systems expensive to install?
The cost of installing a greywater system varies based on complexity and local regulations. Basic systems can start at a few hundred dollars, while more advanced setups may exceed several thousand dollars.
Do I need a permit to install a greywater system?
Yes, many regions require permits for greywater systems to ensure compliance with health and safety regulations. Check local guidelines before installation to avoid fines.
Can I use greywater on my garden?
Yes, treated greywater is safe for irrigating gardens and landscapes. However, it’s important to follow local regulations regarding which plants can be watered with greywater.
What are common concerns about greywater systems?
Common concerns include potential health risks, odor issues, and system maintenance. Regular upkeep and proper treatment can mitigate these risks effectively.


