Understanding BTU Ratings: A Guide to HVAC Efficiency and Comfort
Key Takeaways
-
BTUs, or British Thermal Units, is a measurement of energy used to describe the heating and cooling capacity of HVAC equipment. It’s a measure of the energy needed to increase the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
-
Getting the right BTU calculations is crucial to choosing HVAC equipment that adequately fits your space to ensure you have the best comfort and energy efficiency.
-
To calculate BTU needs, measure room size in square feet, account for ceiling height, evaluate insulation, and consider factors like climate, windows, and occupants.
-
Matching BTU ratings to system capacity helps minimize inefficiencies. This avoids frequent cycling for oversized systems and makes sure undersized systems can deliver sufficient heating or cooling.
-
Not only does properly sized HVAC systems keep people more comfortable at lower energy costs and increase the equipment’s lifespan, it helps reduce the industries overall environmental impact.
-
Misunderstandings, such as the idea that larger BTU ratings provide better performance, often result in inappropriate system sizing and wasted energy.
Understanding BTU ratings for HVAC equipment is the first step to choosing the right HVAC system to heat or cool your home or business. BTU is short for British Thermal Unit. It is the measure of energy needed to raise or lower the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
This rating directly impacts the efficiency and capacity of HVAC units and is a valuable tool for users to help identify the right equipment to meet their unique needs. Whether you’re buying a window AC unit, central heating system or portable heater, the BTU rating is the most important number. It ensures you’re getting top performance and energy efficiency.
Choosing the right size avoids problems such as hot or cold spots or unnecessary energy expenditure. By learning how to interpret BTU ratings, homeowners and professionals can make informed decisions, leading to more comfortable and cost-effective spaces.
What Is BTU in HVAC
Definition of BTU
A BTU, or British Thermal Unit, is a basic unit of heat energy used in HVAC to quantify heat energy. Specifically, it represents the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
This simple definition goes a long way to clarify why BTUs are key to understanding heating and cooling systems. So when you see a furnace with a 40,000-BTU rating, that’s telling you how powerful it is.
This unit is capable of producing 40,000 BTUs of heat energy per hour. Accurate BTU ratings are paramount. They indicate how efficiently a system produces or delivers desired temperatures, keeping your equipment from working too hard or too easy.
BTU as a Measurement of Energy
BTUs are a measure of the energy produced by HVAC systems. Unlike watts or kilowatt-hours, commonly used in electrical systems, BTUs are all about thermal energy.
So for example, air conditioners need at least 20 BTUs per square foot to cool a room effectively. Proper, precise measurements are key to achieving peak performance.
Simply having a unit with the wrong BTU rating costs you money in wasted energy and/or not enough comfort. For example, Florida’s climate zone 2 recommends cooling capacity ranging from 30 to 50 BTUs per square foot.
Of course, this range varies based on your unique needs.
Importance of BTU in HVAC Systems
BTU ratings directly affect system performance, energy efficiency, and home comfort. This means a heating unit with 90% efficiency uses energy 10% less than a 80% efficiency heating unit.
For example, a 40,000-BTU furnace running at 90% efficiency will use 4,000 fewer BTUs of energy than a similar 80% efficient unit. Choosing the right BTU rating means your HVAC system will run efficiently without wasting energy.
HVAC experts trust the Manual J calculation method to focus on precise BTU needs. They factor in climate zones and square footage to deliver tailored recommendations.
How to Calculate BTU Requirements
Knowing how to calculate BTU requirements will help you choose the right HVAC system to keep your home comfortable without wasting energy.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
-
Measure the room Measure the length and width of the room in feet. Then, multiply those two figures together to determine the total square footage. For instance, a 20 ft by 15 ft room would be 300 sq. ft. The larger the space, the higher the BTU ratings need to be.
A good rule of thumb is to require 24,000 BTUs per 1,000 square feet. Therefore, a 1,000 square foot house generally needs 30,000 to 50,000 BTUs for central air conditioning. Online BTU calculators make this process easy, allowing you to enter your room’s dimensions to get a rough estimate in seconds.
-
Ceiling height affects air volume Ceiling height directly impacts the air volume in the space. This means a typical 8 ft ceiling has less air than a 12 ft ceiling to heat or cool. Multiply room square footage by ceiling height to compensate.
A 300 sq. Ft. Room with a 12 ft ceiling will need more BTUs than one with 8 ft ceilings. The greater air volume in the taller space adds to the need for heating or cooling.
-
Insulation quality plays a role in thermal retention Since well-insulated homes lose less heat, they require fewer BTUs. Homes with fiberglass or foam insulation are really good at saving energy. Spaces with bad insulation allow much more heat to escape, thereby raising BTU requirements.
Before you make any final calculations, check your insulation.
-
Adjust for Climate and Location Geographic location is important. Depending on climate or regions with very pronounced seasonal changes, you may need significantly more BTUs. To put it another way, a home in Phoenix, AZ will require substantially more cooling capacity than one in Seattle, WA.
Consider local weather patterns and how much sunlight your space gets when calculating BTU requirements.
-
Impact of windows and doors Similarly, large windows, particularly those that face south, contribute to increased heat gain, raising the cooling BTU requirement. Single-pane windows have a higher heat loss than double-pane.
The quantity and location of doors has an impact on energy loss as well. For example, you might require additional BTUs for a room with several exits to cool the space evenly.
-
Appliances contribute to heat load Appliances such as ovens, stoves, and even computers contribute to the heat load, making cooling needs even higher. Count up how many of these devices you’ll be using and their total wattage.
For instance, if you have ten 100-watt bulbs, that’s a lot of heat, so you’ll have to compensate in your BTU calculation.
-
Add in Number of Occupants Humans are heat-producing creatures. As a rule of thumb, it’s about 10–15 BTUs per square foot per person. That’s $1,056 a month, which, if you’re a family of four living in a 1,000 sq. ft. home—this becomes significant very fast.
Look at activity levels as well, since more active spaces will require more cooling.
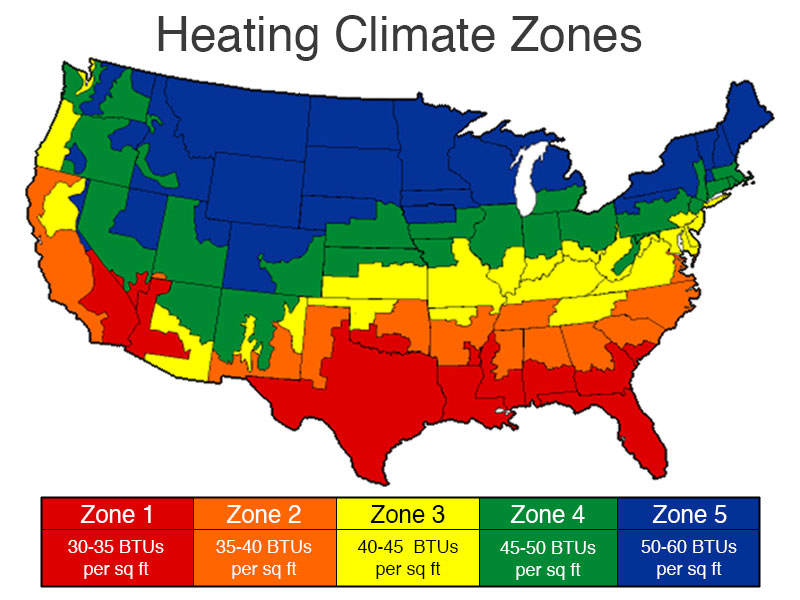
BTU Ratings and System Efficiency
Role of BTU in Energy Efficiency
BTU ratings play a huge role in the energy efficiency of HVAC systems. They set the maximum amount of work each unit is allowed to do. Proper ratings mean the system runs at the efficiency it was designed to operate, saving energy that would otherwise be wasted.
A system rated at 90% efficiency uses less gas. It operates for fewer hours each day while maintaining the best possible heating or cooling output. This level of precision ensures less energy is consumed, resulting in more money left in household budgets.
Systems with accurately determined BTU ratings help to promote sustainability by reducing wasted energy. An air conditioner with a SEER rating of 12 indicates an excellent balance between performance and energy consumption. This is a ratio that’s computed by taking 60,000 BTUs of cooling and dividing that by 5,000 watt-hours of electricity.
Matching BTU Ratings to System Capacity
Properly aligning BTU ratings with system capacity is important for proper operation. In places such as zone 2 of Florida, it’s advised that air conditioning systems deliver 30 to 50 BTUs/sq ft. This makes sure only spaces that need to be cooled are sufficiently cooled without overworking the system.
Mismatched ratings—such as installing an over-large unit in a small space—lead to short cycling and wasted energy. As a result, it leaves hot and cold spots across the entire area. Consulting professionals helps achieve the correct match, avoiding discomfort and inefficiency.
Impact of Incorrect BTU Ratings on Efficiency
Oversized units may cool or heat quickly but fail to maintain consistent temperatures, while undersized systems struggle to meet demands, leading to overwork and higher energy bills. Imprecise BTU calculations can lead to premature wear on an HVAC system, driving up repair and replacement costs in the long run.
For example, larger spaces or less insulated areas may require more BTUs, but overestimating can result in subpar performance.
Choosing the Right BTU Rating
Choosing the right air conditioner BTU rating ensures your HVAC system will work effectively and efficiently, creating a comfortable space while saving you money on energy costs. Consider these key points when deciding.
-
Steer clear of oversized HVAC systems which waste energy and money.
-
Avoid undersized systems that can’t deliver enough heating or cooling.
-
Request expert evaluations to make sure you get the right BTU calculations specific to your home.
Avoid Oversized HVAC Systems
Though it may seem like a good idea to oversize your HVAC systems, the consequences could be quite serious. That’s because these units often short cycle.
That is, they turn on and off a lot. This not only wastes energy, but it puts additional strain on the system, shortening its lifespan. A unit with a higher BTU rating than necessary for a 1,000-square-foot home in Florida will end up cycling too quickly.
This quick on and off action leaves you with extreme hot or cold spots, creating an uncomfortable environment. When a system is properly sized, it runs comfortably, with an even temperature distribution and lower energy consumption.
Prevent Undersized HVAC Systems
Undersized systems don’t have the capacity to keep up with demand, which results in uncomfortable indoor temperatures and increased running costs. A unit with too few BTUs will run constantly and won’t ever keep you comfortable.
For example, in colder climates, a heating unit with too few BTUs would result in the rooms never getting up to an acceptable temperature. Doing things the right way—ensuring accurate BTU calculations using methods such as the Manual J system—prevents concerns like these, resulting in a more comfortable and efficient home.
Importance of Professional Assessment
Consulting HVAC professionals is essential for determining the correct BTU rating. Experts evaluate factors such as home size, insulation, and climate zones.
For instance, most of Florida falls into zone 2, requiring specific BTU ranges for optimal performance. Professionals consider system efficiency, like choosing a 90% efficient unit to save energy.
Their evaluations result in systems that work effectively and last longer.
Benefits of Proper BTU Sizing
Improved Comfort Levels
When the BTU rating of your HVAC system is proper for your home, you’ll experience better indoor temperature consistency from morning until night. When the system is properly sized, it isn’t overworking or underworking, which establishes an even, comfortable space and a healthier building overall.
An oversized unit may cool the air so fast that your space feels uncomfortable, damp, and clammy. An undersized unit has a hard time keeping up, leading to inconsistent cooling or heating. Proper BTU sizing guarantees the system will be able to keep your space comfortable and improve quality of life for everyone under your roof.
Enhanced Energy Savings
Properly matching BTU ratings to your home’s needs can greatly reduce excessive energy use. An undersized unit will run more often and for longer stretches, consuming more energy and increasing utility costs.
A correctly sized HVAC system runs more wisely, minimizes energy waste, and conserves energy. Properly sizing a new unit can save households 10–20% on their energy bills. This is why proper BTU sizing is essential to realize the highest financial benefit and ensure long-term affordability.
Prolonged Equipment Lifespan
Properly-sized HVAC units are under less strain, reducing wear and tear over time. This results in overheating or overcooling, as undersized units are forced to work harder than necessary.
This causes untimely failures and increases the cost of repair. Proper BTU sizing also helps parts operate more smoothly, which prolongs the life of all components and minimizes unexpected breakdowns. Proper regular maintenance, along with proper BTU sizing, guarantees both longevity and efficiency.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Efficient HVAC systems with the proper BTU rating consume less energy, which can be leveraged to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This not only reduces your carbon footprint, it creates a more sustainable home in the long run.
By maximizing energy efficiency, you’re making a positive impact on the environment. That’s how the right BTU-sizing helps you save cash and climate.
Common Misconceptions About BTU Ratings
While it’s crucial to understand BTU ratings for air conditioning units, misconceptions can misguide consumers and complicate the HVAC installation process.
-
Bigger BTUs always mean better performance.
-
Each space needs the same BTU rating no matter the size, orientation, or occupancy.
-
Higher BTU ratings guarantee energy efficiency.
Bigger BTU Always Means Better Performance
Other folks may believe that a higher BTU rating is always indicative of superior HVAC performance. Here’s the deal — if you oversize your system, you’re going to run into issues.
For instance, an air conditioner that has too many BTUs will cool a room too fast. Though this may seem great, it doesn’t provide nearly enough time to adequately remove humidity. The impact can be a cold, clammy atmosphere rather than pleasing cooling.
If a unit is undersized, it will be unable to keep up with demand. Now it has to run all the time and will wear out much quicker for it. This year-round run-time increases energy costs and shortens the life expectancy of the system.
Correctly sized, according to square footage and considerations such as insulation or climate, provide optimum efficiency and comfort.
All Spaces Require the Same BTU
It can be tempting to think that every space needs the same BTU provided, but that is not the case. For example, a well-insulated room will need fewer BTUs than a poorly insulated space.
Common Misconception #2— The colder the climate, the fewer BTUs needed to heat a home. A like home in a more temperate area requires fewer BTUs.
Individualized calculations are key. Considerations such as room dimensions, ceiling heights, and even how many people are occupying a space at any given time all factor in.
As a rule of thumb, 20 BTUs per square foot is a good ballpark, but that can differ depending on your surroundings. Climate zones and conditions — such as sun exposure versus shade — are key factors.
Conclusion
Having a basic understanding of BTU ratings will help make choosing the right HVAC equipment a simpler task. It saves you money by ensuring equipment matches your space, prevents energy waste, and maximizes comfort. With a properly sized system, you’ll enjoy more even temperatures and lower utility bills. An oversized or undersized unit may lead to hot and cold spots, more expense, as well as increased equipment wear and tear. Being mindful of BTU ratings saves a lot of hassle later on.
To ensure you do it correctly, begin with some simple calculations. Next, look closely at your space and figure out exactly how much heat or cooling you require. Whether you’re replacing old equipment or going in new, take these lessons to ensure you’re making the right decisions. As always, for the best results, consult with a knowledgeable HVAC professional. Making smart decisions today will save time, money and stress down the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does BTU mean in HVAC?
BTU, an acronym for British Thermal Unit, measures the energy output of HVAC systems, indicating how much heat they can safely add or remove from a space. A higher BTU rating signifies greater cooling or heating capacity, essential for efficient heating and cooling.
How do I calculate the BTU requirements for my home?
To determine BTU ratings for your air conditioning unit, consider factors like room size in square feet, insulation, and climate. A good rule of thumb is 20 BTUs per square foot for cooling, so consult Carrollton HVAC experts for accurate load calculations.
Does a higher BTU rating mean better efficiency?
The higher the BTU rating, the more powerful the air conditioning unit is. Efficiency comes down to proper sizing and quality of various HVAC systems. Oversized HVAC units may waste energy and drive up costs.
What happens if I choose the wrong BTU rating?
An undersized HVAC unit pushes harder to maintain comfort, while an oversized air conditioning system short-cycles, wasting energy and increasing utility expenditures due to inefficient energy usage.
Can I size HVAC equipment myself?
So it’s always best to leave it to the experienced HVAC professionals. They’ll consider factors such as room size, insulation, and climate to determine the ideal BTU rating for maximum energy efficiency.
Are all BTU ratings the same across HVAC systems?
No, BTU ratings are system specific, and it’s crucial to understand that different HVAC units like a heat pump and an air conditioner can share the same BTU output while operating very differently for heating and cooling.
What’s the biggest benefit of proper BTU sizing?
With accurate BTU sizing for your HVAC system, you’ll enjoy energy efficiency and cost savings, along with consistent comfort throughout your home and improved HVAC unit lifespan.


